It may not be immediately obvious how psychology has a place in your business. It’s often associated with the mind and psychiatry, but in reality, psychology plays a role in everything we do. In essence, it is the study of human behaviour and focuses on how we think, learn and behave. Understanding human behaviour is actually integral to every business.
How does psychology fit into business?
If you have customers, we need to understand their motivations, feelings, desires and drivers. This should underpin everything we do as a business owner. Without understanding what our customers want and need, we can’t know how best to serve them.
Consumer psychology
Consumer psychology is basically the study of what makes people buy things. A consumer psychologist will be involved in research to determine the underlying cognitive processes involved in consumer choices and how people respond to marketing, social influences and advertising.
In short, we can all apply consumer psychology to our businesses, without being a psychologist. It is all about understanding how to convert leads to customers and there are several principles to understand.
Understanding human drivers
Quite simply put, what drives us to do what we do? In the case of consumer psychology, what drives people to buy a product or service? Understanding this is key to knowing what motivates our customers and what will get their attention. If we can tap into these, we can appeal to a certain side of our buyer and help them fulfil one of their needs.
Why do we buy?
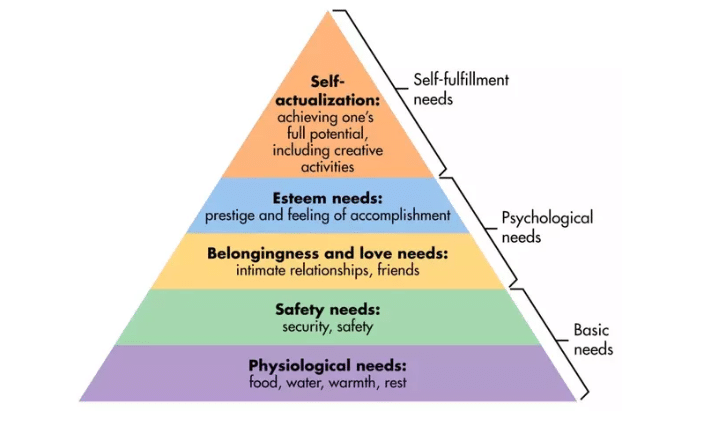
Everything we do comes down to fulfilling a need. Arguably, the most famous research to date on the subject of human needs is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Human Needs, which can be applied to consumer behaviour. Maslow believes that human behaviour is directed by our need to meet either a basic, psychological, or self-fulfilment need. Our needs are as follows:
- (Basic) Physiological needs- These are our most fundamental needs to ensure we stay alive, such as food, water and sleep. For businesses, this may be food, drink, clothes, beds, etc.
- (Basic) Safety needs- These are things like security, safety reducing risk. This may be in the form of a house, security systems, utility services, insurance and medication.
- (Psychological) Belonging and love- These needs incorporate our desire to fit in and feel loved. In terms of the things we buy, this could be identifying with a certain brand, group or passion such as a band. It could be clothes, magazines, photographs, joining clubs
- (Psychological) Esteem needs and accomplishment- This could be sought through art, fashion, music, courses and classes.
- (Self-fulfilment) Self-actualisation and reaching potential- This could be about establishing a unique identity or about social status and can be targeted through products like clothes, cars, jewellery, holidays, courses and travel.
Why do we take action?
Understanding what makes people tick and what needs we are fulfilling when we look to buy something is one thing, but how do we translate that into actually getting people to part with their money? According to Aristotle, there are 7 things that cause humans to take action. When it comes to selling a product, making sure we make use of these will help us close the deal.
Chance
Make sure your customers know exactly what you want them to do. In marketing terms, this would be a strong call to action. Don’t be ambiguous. Tell them about your great product and then let them know you want them to buy it.
Nature
It’s important that people feel that they are aligned to a product or brand. Pick a niche and make sure that your products, branding and values are inline with the person you are targeting. If they don’t feel that your product or service represents them, they won’t buy it.
Compulsion
Whilst us humans can be very calculated about what we are looking for, we are also very impulsive. Impulse buys are a great way to get sales. Look at how you position things and price things so that customers are open to buying from you on a whim.
Habit
We are creatures of habit. Create a brand that people want to come back to. Give incentives and make consumers feel special and valued. In return they will be loyal.
Reason
Consumers need a reason to buy. This comes back to what we said above. Appeal to one of their needs and give them a reason to pick your product.
Passion
Within your niche, you will know what gets your customers all fired up. Appeal to their passion, whatever that may be. If they are passionate about a cause, donate to it with every sale, if it is the environment that they get fired up about, ensure products are recyclable.
Desire
Tapping into a customer’s desire, is less about the product and more about creating a story and a feeling. How will having your product or service make them feel? What goal will it help them achieve?
Simple steps for understanding your ideal customer
If psychology is new to you and this all sounds a bit much, think of it all in terms of understanding the needs and desires of your customers. We can do this quite simply by implementing the following:
1. Talk and listen to your customers
This could be through a variety of platforms and means. You can use something formal like a focus group, market research surveys, feedback questionnaires or by less structured means like answering questions over social media, in person, or by analysing and responding to customer service queries.
However you do it, it’s important to find out what the product means to them, what they use it for, likes and dislikes, how it makes them feel, what your brand means to them.
2. Watch customers
This is less creepy than it sounds. Lots of big brands pay consumers to spend time with them while they use their products or to film themselves using them. For example, Ford engineers pay consumers to spend the day with them whilst they drive their car, going about their daily business. They watch how they unload the car, how they cope in rush hour and how they park etc. It gives a great insight into what is used, valued and any difficulties.
3. Beta testing
New products or services can be tested on a small group of people known as beta testers. Beta testing usually means offering your product to a small number of people either for free or at a reduced cost, in exchange for feedback. This initial stage allows you to identify what customers think of your product, whether it is appealing to your target customer and any suggestions for improvements. This group can be used to test ideas and future innovations as a cross section of your market.
4. Feedback
Throughout your business journey, always make sure you are asking for, and analysing feedback. Simply gathering feedback means nothing if you don’t use it to discover whether your services and products are still relevant to your customers. By ensuring that your customers are buying your products and understanding why, you will always be able to appeal to their needs.
Leverage decades of business experience from every angle to get to the heart of your business challenges—with insights and a road map to inspire business possibility. Contact us for more.